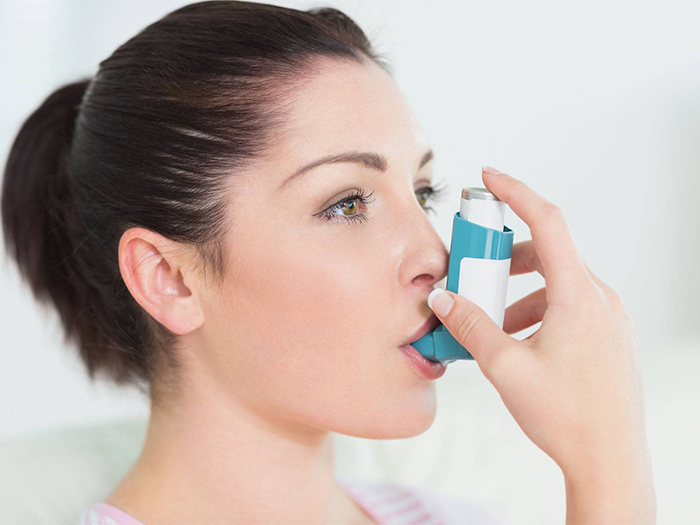
What is inflammation of airway in Asthma?
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the lungs. Approximately 25 million Americans and 1 in 10 children suffer from asthma. The disease involves the airways or bronchial tubes to allow air passage inside and outside of the lungs. People with asthma have sensitive airways in their lungs that react to triggers, causing a ‘flare-up’. During flare-ups, the muscles around the airways squeeze tight, gets swollen and become narrow with mucus. This causes airway inflammation and makes it difficult for the air to move in and out of the lungs causing asthma symptoms like:
- Coughing
- wheezing
- tightness in the chest
- shortness of breath
As soon as the symptoms flare up, you can have an asthma attack. This may be seen that not all the people who have asthma develop these symptoms. Your doctor will diagnose airway obstruction based on the medical tests, medical history and physical examination.
Interesting Asthma Facts:
- Asthma is a worldwide health problem that is under-diagnosed and under-rated.
- Most common non-communicable disease among the children.
- As per WHO estimation approx. 235 million people currently suffer from asthma.
- In children, boys are more likely to develop asthma than girls, but in adults, women are more likely than men.
- Approximately 10% of asthma sufferers develop severe asthma.
- One of the major cause of severe asthma is cigarette smoking that includes both first and second hand smoking.
- African-americans shows increased incidence of asthma.
- Annual estimated cost of asthma is $56 billion.
- Asthma is often hereditary.
- Currently, 26.5 million Americans have asthma. Of the 26.5 million, 20.3 million (8.3%) are adults and 6.1 million (8.3%) are children.
What are the types of Asthma?
Asthma is also referred to as bronchial asthma as it affects the bronchi in lungs. To understand asthma it’s important to understand the types of asthma discussed below:
- Allergic Asthma
- Non-allergic Asthma
- Occupational Asthma
- Cough Variant Asthma
- Exercise- Induced Asthma
- Nocturnal Asthma
Allergic asthma:
Genetics probably play an important role in asthma and allergies. This tends to run in families and may be hereditary. It’s more likely to be seasonal as it goes hand in hand with the seasonal allergies as well. The symptoms starts after inhaling any of these allergens listed below:
- Pollens
- Dust Mites
- Pet dander
- Molds
Non-allergic Asthma:
Also called as intrinsic asthma. The allergens/irritants in the air are not related to allergies trigger. These allergens includes:
- Perfumes
- Cold air
- Household cleaning products
- Air fresheners
- Viral illness
- Smoke
- Household cleaning products
Occupational Asthma:
A type of asthma induced by the allergens in the workplace including woodworks, textiles, manufacturing and farming. The allergens includes:
- Dyes
- Rubber latex
- Chemicals
- Fumes
- Dust
- Harmful gases
Cough Variant Asthma/inflamed airway coughing:
The type of asthma is characterized by a persistent dry cough. It doesn’t shows clear symptoms of wheezing and shortness of breath. Inflamed airways coughing can lead to a full blown asthma flares that includes various common symptoms. The triggers usually include
- Bronchitis and other upper respiratory infections
- Post nasal drip
- Acid reflux and GERD
- Blood pressure medications
- COPD and chronic bronchitis
Exercise-Induced Asthma:
The type of asthma that usually affects people within a few minutes of starting any exercise, physical exertion and 10-15 minutes after physical activity.
Nocturnal Asthma:
The Nocturnal Asthma symptoms start worsening at night. The triggers may include:
- Body’s natural sleep cycle
- Pet dander
- Psychological stress
- Obesity and excess fat
- Increased mucus production
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Psychological stress
What Causes Airway Inflammation in Asthma?
The causes of inflamed airway in asthma are listed below:
- Genetics.
- Contact with the environmental allergens, irritants and respiratory infections have been linked with the development of asthma.
- The inflammation in the airways may be triggered by different things among different individuals and gets the muscles around the airway to contract due to which the lining of the airways start developing extra mucus with a further obstruction in the airflow.
- Exposure to certain harmful chemicals and dust particles may also play a significant role in the onset of asthma symptoms.
- Strong odors can act as triggers.
Symptoms & Triggers of Airway Inflammation in Asthma
The symptoms of airway inflammation in asthma may range from cough and cold that lingers for days or weeks to a sudden breathlessness emergencies. There are few people who find that in many conditions their symptoms may get worse and it’s possible to avoid certain triggers that particularly helps to reduce these symptoms. The symptoms include:
- Chest tightness and pain
- Breathlessness/shortness of breath
- Trouble sleeping
- Coughing
- Weezing
Things that may trigger inflammed airway generally includes:
- Pollens and molds
- Respiratory infections
- Heavy exercises
- Certain medicines
- Smoking
- Fumes and chemicals
- Dust mites
- Stress and Emotional anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Some foods
- Allergies to animals
Some people may develop symptoms when exposed to a certain triggers and for some the asthma may get worse while coming in contact with the allergens.
How Your Airway Get Obstructed?
The airways to the lungs are completely open during normal breathing that allows air to move in and out of the lungs freely. Asthma causes the airways to change in the following ways:
- The airway branches leading to the lungs become sensitive and reactive to all kinds of asthma triggers
- The linings of the airway swell and become inflamed
- Mucus clogs the airways
- Muscles tighten around the airways
- The lungs have difficulty moving air in and out
These changes leads to the narrowness of the airways causing difficulty in breathing and finally an asthma attack.
How is Asthma Diagnosed?
To diagnose asthma, your doctor will ask about your medical history and perform few physical examinations. They may suggest chest x-ray, lung function test, sinus test or other tests.
- Medical History of the patient – This may include questionnaire to understand eczema symptoms and causes. This may include questions related to:
- Family history of asthma
- Lifestyle
- Allergies history
- Current physical problems
- Exposure to any environment
- Stress levels etc

- Lung function tests – Your doctor may suggest you to take one or more breathing tests also called as lung function tests in order to measure your breathing. The test is often carried out before and after the inhalation of bronchodilator, a medicine that opens your airways. If there’s any relief from the bronchodilator, then you probably have asthma. Your doctor may also prescribe few tests like:
- Peak airflow
- Spirometry
- Provocation tests
- FeNO tests
- Allergy tests
- Physical Examinations – Physical diagnosis allows your doctor to review your health. They may look at your eyes, skin, throat, chest, lungs and ears.
Airway inflammation treatment
Asthma has no cure but its symptoms can be controlled with an effective asthma management and treatment. This involves taking your medications as directed by the physician and learning to avoid the asthma triggers.
- Controller medications are taken daily that include corticosteroids (fluticasone, budesonide, mometasone, ciclesonide, flunisolide, beclomethasone and others).
- LABAs are symptom-controllers that are helpful in opening the airways. It should never be recommended as a sole therapy for asthma.
- Leukotriene modifiers are the oral medications that particularly includes zafirlukast, zileuton, and montelukast.
- Anticholinergics also help in opening the airways and are used as a maintenance therapy for asthma.
- Quick relief medicines like inhaled bronchodilator, albuterol, pirbuterol can be used for asthma relief. These acts as a short relief beta agonists. These medicines do not take place of controller medicines.
People with asthma are generally at a high risk of developing respiratory infections such as influenza and pneumonia. That’s the reason asthma sufferers needs to be vaccinated annually. With a perfect asthma management plan, care and treatment, you can minimize the asthma symptoms and lead a healthy life.
Related Posts: