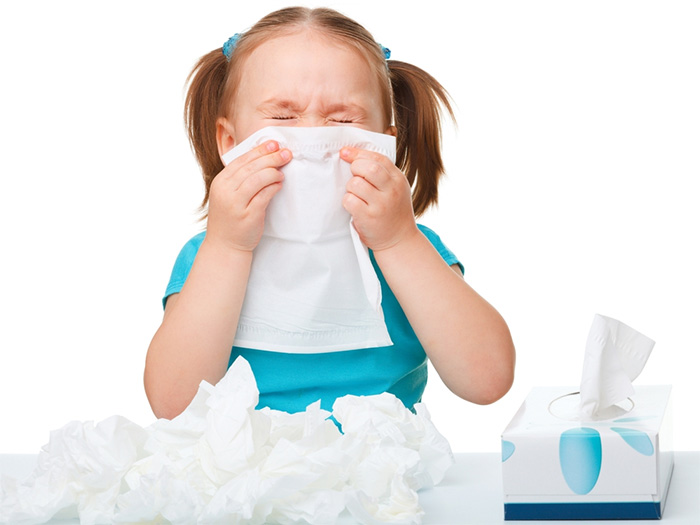
Each year several millions of US children and adults are claimed to be at risk of allergies and their severe consequences. An allergy is defined as the reaction of the immune system generated against a harmless foreign substance, known as an allergen. The substance can be anything you consume, inhale, touch or inject in the body. Also, the allergen might trigger a reaction in your body but cause no response in others.
There are several things that can cause an allergic reaction. The severity of the reaction depends on an individual’s defense mechanism and its potential to fight against allergens. In most of the cases, children in the USA have been found to be sensitive towards the following substances and developed allergies as a result of:
- Pollen
- Certain classes of foods
- Animal Dander
- Dust Mites
- Insect Stings
- Mold
- Medication
- Latex
- Cockroaches
The symptoms of allergy includes coughing, sneezing, itchy eyes, a runny nose and a scratchy throat. In severe cases, it can result in rashes, hives, low blood pressure, breathing trouble, asthma attacks, and even death. The results may vary from mild cases to life-threatening cases. On an average, 1 in 5 Americans suffers from some sort of allergy.
Food Allergies
Food allergy is a very common condition amongst the American children. Approximately, 160 foods are susceptible to causing allergic reactions. According to FDA, following 8 foods are recognized as the most common allergenic foods:
- Milk
- Eggs
- Fish (e.g., bass, flounder, cod)
- Crustacean shellfish (e.g., crab, lobster, shrimp)
- Tree nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts, pecans)
- Peanuts
- Wheat
- Soybeans
These specific foods are identified to be accountable for 90% of the food allergic reactions. However, in few cases food allergy may be confused with food intolerance, hence, medical intervention is necessary. Also, you must know the symptoms of food allergies in children.
The most common food allergic reactions include:
- Hives
- Rash
- Itchy sensation in the mouth
- Swelling of the face, tongue, or lip
- Vomiting and/or diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Coughing or wheezing
- Dizziness
- Light headedness
- Throat and vocal cords swelling
- Difficulty in breathing
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms may show within few minutes to few hours after the consumption of the specific food. There is no cure for food allergies, except avoiding the consumption of the food allergen. In order to prevent severe health conditions, early detection and management of allergic reactions to food are necessary for your child.
Skin Allergies
In certain cases, allergens may develop skin allergies or can trigger a skin disorder. Eczema, contact dermatitis, hives, swelling are common skin conditions that are likely to be triggered or caused as a result of allergies.
Common symptoms of eczema or skin allergy in children:
- Rash
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Raised bumps
- Scaling (flaking of skin)
- Cracked skin

The Connection Between Eczema and Allergy
Eczema is a common skin disorder that affects approx. 15% to 20% of babies in the U.S. The cause of the skin condition is unknown but it is often linked with the genes and environmental factors.
The family history of eczema, allergies, hay fever or asthma can also develop this skin condition in the baby. Your child may not have developed eczema as a result of allergens but their condition can worsen in the presence of specific substances that cause an allergic reaction. Additionally, children with eczema are more prone to develop food allergies and vice versa.
Avoid allergy triggers to prevent Eczema flare-ups
To manage eczema in your child, ensure to rigorously follow a daily routine that includes proper moisturization, nutritious diet, and intake of prescribed medication. This also aids in avoiding things that trigger allergies. You must also follow the suggested tips for the child:
- Keep a track of the conditions and situations, when the eczema symptoms of the child worsened. This can help determine the substances that might have triggered the skin condition. You can share your findings with the concerned dermatologist during the next visit to obtain a better treatment.
- You must keep the child away from things that can irritate or agitate their skin. A few common irritants and allergens include wool, soaps and detergents, perfume, chemicals, sand, and cigarette smoke.
- The child must avoid coming in contact with allergy triggers like pollen, mold, pet dander, dust mites, as they may cause eczema flare up. Ensure that the mattress and pillow covers are dust-proof, they must stay away from animals, try and remain indoors when the pollen counts are high.
Allergy Facts and figures for the U.S.
How many children are affected by allergies in the U.S.A ?
Allergies are increasing. They affect as many as 40% of children.
Allergic disease, including asthma, is the fifth leading chronic disease in the U.S. in people of all ages. It is the third most common chronic disease in children under 18 years old.
Results from a 2009-2010 survey of more than 38,000 children indicate that 5.9 million children, or 8%, have food allergies. That’s 1 in 13 children or roughly two in every classroom.
In a 2007 survey of 9,500 children, 3.9% were reported to have a food or digestive allergy within the past year.
How many people get sick because of Allergies?
Allergic conditions are the most common health issues affecting children in the U.S. People visit the emergency room about 200,000 times each year because of food allergies. Almost 10,000 people stay in the hospital each year because of food allergies.
How Common are skin allergies Amongst children in the USA?
- In 2012, 8.8 million children had skin allergies. Children age 0-4 are most likely to have skin allergies.
- In 2010, African-American children in the U.S. were more likely to have skin allergies than white children.
How Common are Food Allergies Amongst children in the USA?
Peanut is the most common allergen. Milk is second. Shellfish is third. Between 2004 and 2006, an average of 9,500 children received in-patient hospital care for food allergies each year.
In 2014, 4 million children in the US have food allergies. Also, 38.7% of food-allergic children have a history of severe reactions. In children with food allergies, 30.4% are allergic to multiple foods.
Compared to children who don’t have food allergy, children with food allergy are two to four times as likely to have other allergic conditions, such as asthma or eczema. Caring for children with food allergies costs U.S. families nearly $25 billion annually.
*Sources:
Also Read This: