What is Neurodermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus)?
Lichen simplex chronicus or neurodermatitis is a form of eczema that is characterized by severe itching and scratching. It usually starts as an itchy patch on the back of a neck, scalp, shoulders, feet, ankles, wrists and hands.
This form of skin ailment commonly affects the anal and genital areas; particularly developing in the scrotum or vulva. The itch-scratch cycle fuels the neurological skin disorder that results in irritated nerve endings of the affected area.
Frequently scratching the already damaged and fragile skin patches makes it itchier, thicker, discolored and leathery
Neurodermatitis Symptoms
The most prominent neurodermatitis symptoms include:
1. Itch: The onset of the skin condition is marked by an itchy patch on the outer dermis. Most of the people with neurodermatitis tend to develop just 1 or 2 such patches but in rare cases, the skin ailment may result in several itchy patches. People frequently rub or scratch the affected areas. They feel itchiest while relaxing or in stressful conditions.
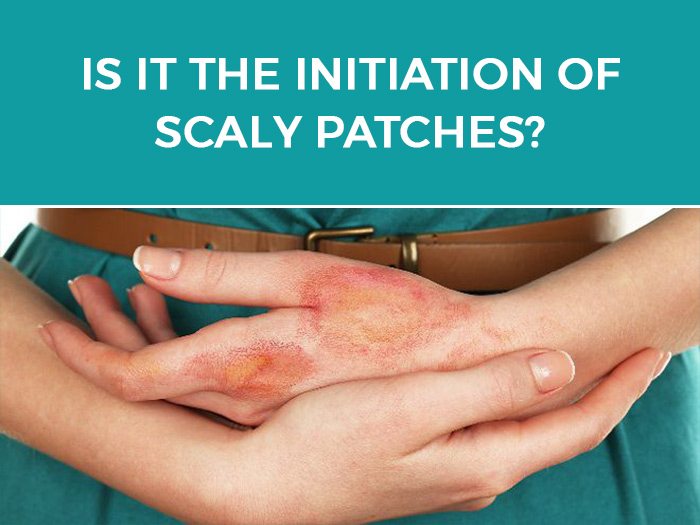
2. Red or violet-colored raised and rough patches: A scaly, red or violet-colored patch forms as a result of repeated scratching or rubbing of the itchy area.
3. The skin may thicken and look leathery with brown colored patches because of the extensive scratching.
4. Your habit of repeatedly or sporadically scratching the affected area may turn it into a wound (a sore that bleeds) that becomes an easy target of microbial infection. If the wound deepens, it may lead to scarring of the skin.
5. In case the wound gets infected, a crusty layer is formed on the affected area that oozes fluid. Pus-filled bumps may develop in severe conditions.
Causes of Neurodermatitis
Researchers are still determining the exact cause of neurodermatitis. However, the condition may develop due to certain factors like stress, overreaction to tight clothing, insect bite, family or personal history of skin disorders. Sometimes, this type of dermatitis may also occur in combination with a skin allergy.
The symptoms of neurodermatitis get aggravated due to repeated scratching of the itchy patch. However, the skin ailment is not life-threatening or contagious.
Risk factors and Complications Associated with Neurodermatitis
There are certain factors that tend to increase the chances and risk of neurodermatitis development. These factors may include:
- The age and sex: Women are at a higher risk of being diagnosed with neurodermatitis in comparison to men. The skin ailment is more likely to occur between the age of 30 and 50.
- Other skin ailments: Neurodermatitis is more common in those with a family or personal history of eczema, psoriasis or similar skin ailments.
- Stress and anxiety can aggravate the neurodermatitis symptoms, especially the itching sensation.
- Frequent scratching can result in the formation of wound or bacterial infection that can alter the skin color and leave permanent scars. You may develop a habit of scratching and this can also disturb your sleep.
Medical Intervention
You might need to seek medical advice in the following cases:
- When you are frequently scratching the same patch of skin
- The itch is persistent and prevents you from paying attention on your daily routines
- The itchy patch looks infected
The concerned dermatologist can examine the affected area in a proper manner. If required they may even conduct skin tests to confirm if it’s neurodermatitis.
The test results can make clear whether the skin infection and/or itchy reaction is due to some allergy or because of neurodermatitis. It is necessary that you consult a skin specialist as they can provide an accurate diagnosis of your condition and accordingly recommend an effective treatment.
Neurodermatitis Treatment Medication

The dermatologist decides your course of neurodermatitis treatment depending upon the signs and symptoms. The treatment plan varies according to individual needs. However, the following tips are recommended and hold significance for all affected people:
- Preventing scratching, rubbing and touching of the itchy patch is the key to healing the skin.
- Avoiding stress and anxiety can alleviate the symptoms of neurodermatitis.
In most of the cases, the doctor suggests to adopt the below mentioned remedies to treat neurodermatitis:
1. Topical Steroid/Corticosteroid: Topical application of steroids is usually recommended by the dermatologist. Applying the medicine directly to the affected area helps avail maximum benefits. Steroids help prevent itching and reduce inflammation of skin. The doctor may prescribe stronger steroids such as corticosteroid to lessen the itch, redness and swelling. It can help soften the thick and scaly skin developed as a result of neurodermatitis. A non-corticosteroid topical medication such as tacrolimus (Protopic) or pimecrolimus (Elidel) may be prescribed in case corticosteroids have been used for a long duration or they are not suitable for your skin,
2. Cool Compress: You can apply an ice or anti-itch medication to prevent the scratching of skin. You can count on cold compress or soak the affected area for a few minutes before the application of medicine. This softens the skin and helps the medicine penetrate the thick layers easily.
3. Antihistamine: The doctor may prescribe the medication to provide relief against the itch and help you sleep.
4. Moisturizer: Moisturization of the dry skin is an essential way of treating eczema. Eczema makes the skin dry, hence, the need for moisturization increases. Ensure that your skin is properly moisturized to lock in the hydration and prevent dryness. Dryness leads to itching and flare-ups. Check for a suitable oil-based or water-based moisturizer according to your symptoms to soften your skin and making it supple. Prefer ointments and creams over lotions and moisturizers if the skin is too dry.
5. Covering the skin: Cover itchy patch with socks, gloves or gauze wraps to prevent the itch-scratch cycle and help the medication or moisturizer deeply penetrate the affected area. This will aid in quick healing of the skin.
6. Treating the infection: If the affected area is infected, dermatologist may perform tests to diagnose the type of infection. Accordingly, they may prescribe applicators or oral medication (pills, tablets, etc.) to control the infection.
Referral Source:
- https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/eczema/neurodermatitis
- https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/types-of-eczema/neurodermatitis/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/neurodermatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20375634
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lichen_simplex_chronicus
ALSO READ THIS:
- Eczema On Neck & How To Get Rid of Neck Eczema?
- Stasis Dermatitis(Legs Eczema)- Its Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
- Eczema on Hands & How To Treat Hand Eczema in Babies?
- Weeping Eczema & Causes, Symptoms & Home Remedies
- Eczema on Lips & Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention Tips
- Dyshidrotic Eczema & Home Remedies, Causes & Symptoms